Two-stroke Aircraft Piston Engines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of
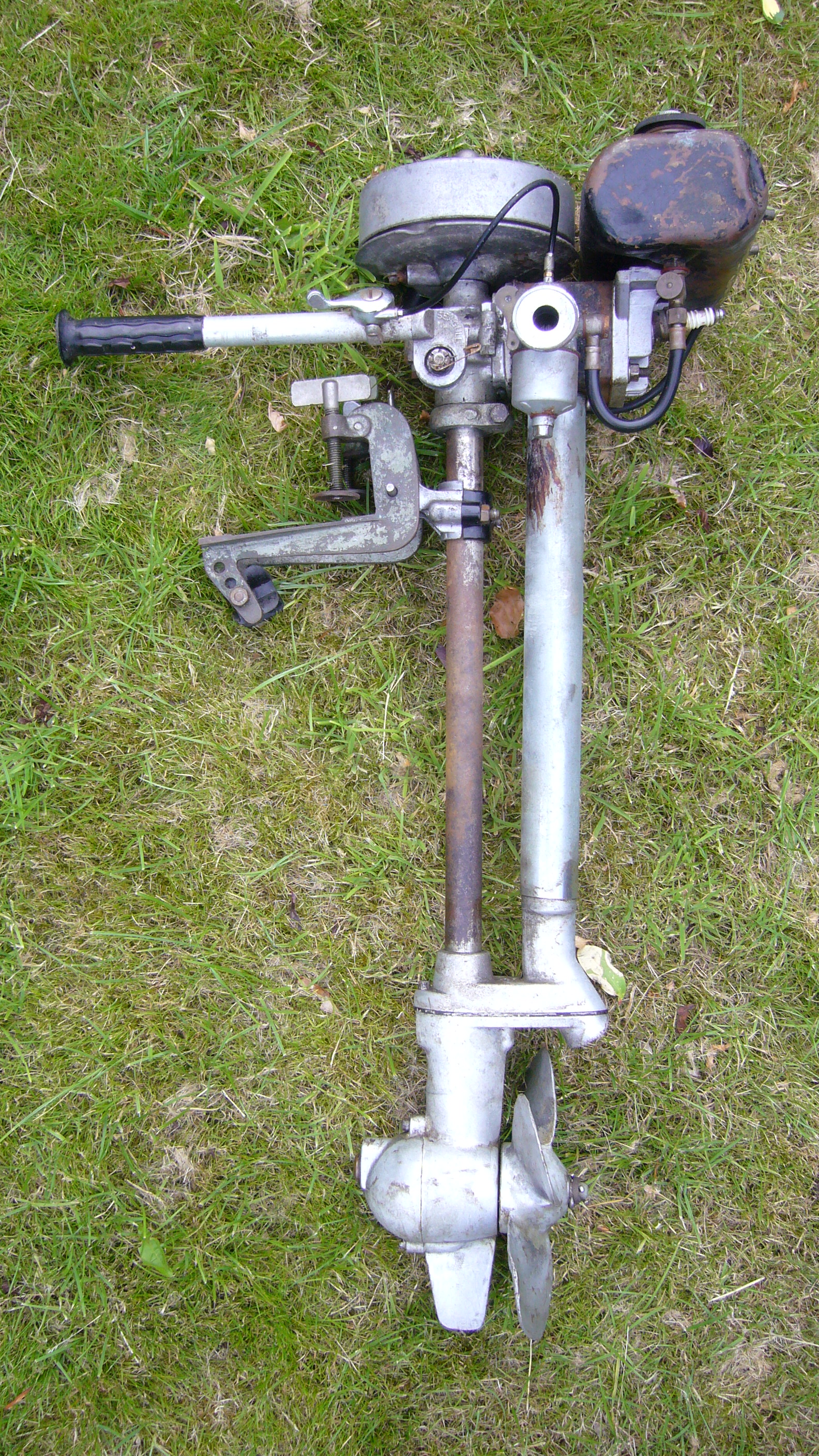

 Two-stroke gasoline engines are preferred when mechanical simplicity, light weight, and high
Two-stroke gasoline engines are preferred when mechanical simplicity, light weight, and high
 Although the principles remain the same, the mechanical details of various two-stroke engines differ depending on the type. The design types vary according to the method of introducing the charge to the cylinder, the method of scavenging the
Although the principles remain the same, the mechanical details of various two-stroke engines differ depending on the type. The design types vary according to the method of introducing the charge to the cylinder, the method of scavenging the
 The reed valve is a simple but highly effective form of
The reed valve is a simple but highly effective form of
 In a cross-flow engine, the transfer and exhaust ports are on opposite sides of the cylinder, and a deflector on the top of the piston directs the fresh intake charge into the upper part of the cylinder, pushing the residual exhaust gas down the other side of the deflector and out the exhaust port.
The deflector increases the piston's weight and exposed surface area, and the fact that it makes piston cooling and achieving an effective combustion chamber shape more difficult is why this design has been largely superseded by uniflow scavenging after the 1960s, especially for motorcycles, but for smaller or slower engines using direct injection, the deflector piston can still be an acceptable approach.
In a cross-flow engine, the transfer and exhaust ports are on opposite sides of the cylinder, and a deflector on the top of the piston directs the fresh intake charge into the upper part of the cylinder, pushing the residual exhaust gas down the other side of the deflector and out the exhaust port.
The deflector increases the piston's weight and exposed surface area, and the fact that it makes piston cooling and achieving an effective combustion chamber shape more difficult is why this design has been largely superseded by uniflow scavenging after the 1960s, especially for motorcycles, but for smaller or slower engines using direct injection, the deflector piston can still be an acceptable approach.
 This method of scavenging uses carefully shaped and positioned transfer ports to direct the flow of fresh mixture toward the combustion chamber as it enters the cylinder. The fuel/air mixture strikes the
This method of scavenging uses carefully shaped and positioned transfer ports to direct the flow of fresh mixture toward the combustion chamber as it enters the cylinder. The fuel/air mixture strikes the

 In a uniflow engine, the mixture, or "charge air" in the case of a diesel, enters at one end of the cylinder controlled by the piston and the exhaust exits at the other end controlled by an exhaust valve or piston. The scavenging gas-flow is, therefore, in one direction only, hence the name uniflow. The valved arrangement is common in on-road, off-road, and stationary two-stroke engines (
In a uniflow engine, the mixture, or "charge air" in the case of a diesel, enters at one end of the cylinder controlled by the piston and the exhaust exits at the other end controlled by an exhaust valve or piston. The scavenging gas-flow is, therefore, in one direction only, hence the name uniflow. The valved arrangement is common in on-road, off-road, and stationary two-stroke engines (
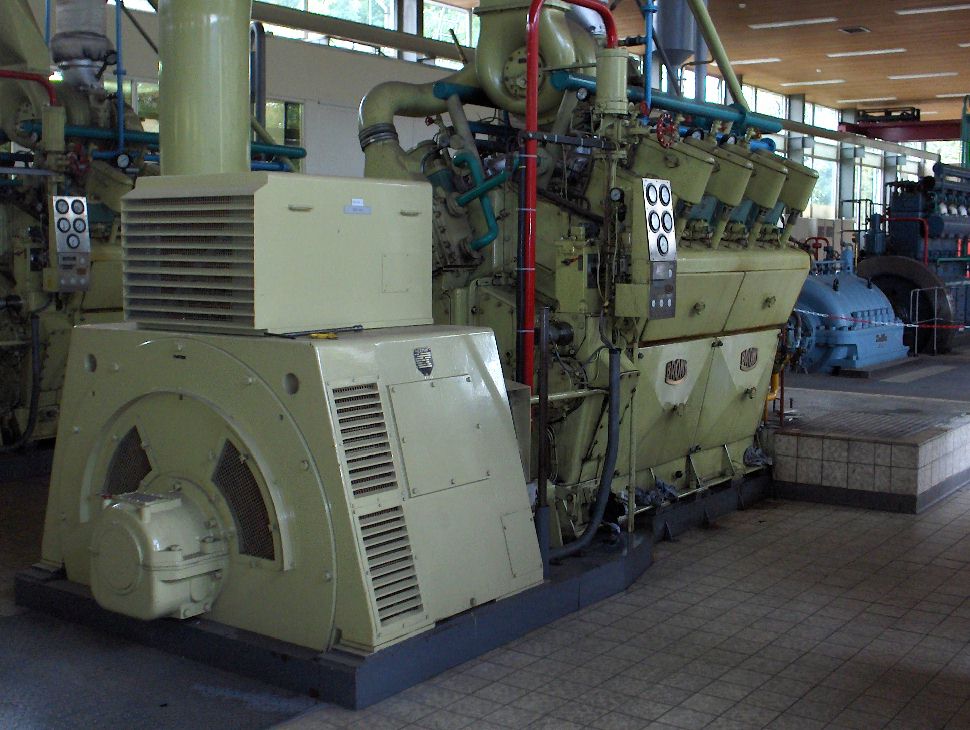 Diesel engines rely solely on the heat of compression for ignition. In the case of Schnuerle-ported and loop-scavenged engines, intake and exhaust happen via piston-controlled ports. A uniflow diesel engine takes in air via scavenge ports, and exhaust gases exit through an overhead poppet valve. Two-stroke diesels are all scavenged by forced induction. Some designs use a mechanically driven Roots blower, whilst marine diesel engines normally use exhaust-driven turbochargers, with electrically driven auxiliary blowers for low-speed operation when exhaust turbochargers are unable to deliver enough air.
Marine two-stroke diesel engines directly coupled to the propeller are able to start and run in either direction as required. The fuel injection and valve timing are mechanically readjusted by using a different set of cams on the camshaft. Thus, the engine can be run in reverse to move the vessel backwards.
Diesel engines rely solely on the heat of compression for ignition. In the case of Schnuerle-ported and loop-scavenged engines, intake and exhaust happen via piston-controlled ports. A uniflow diesel engine takes in air via scavenge ports, and exhaust gases exit through an overhead poppet valve. Two-stroke diesels are all scavenged by forced induction. Some designs use a mechanically driven Roots blower, whilst marine diesel engines normally use exhaust-driven turbochargers, with electrically driven auxiliary blowers for low-speed operation when exhaust turbochargers are unable to deliver enough air.
Marine two-stroke diesel engines directly coupled to the propeller are able to start and run in either direction as required. The fuel injection and valve timing are mechanically readjusted by using a different set of cams on the camshaft. Thus, the engine can be run in reverse to move the vessel backwards.
Two-Stroke Engine
at How Stuff Works * . {{DEFAULTSORT:Two-Stroke All articles with unsourced statements Engine technology Internal combustion piston engines Motorcycle engines Piston ported engines
 A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directio ...
requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time.
Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band
The power band of an internal combustion engine or electric motor is the range of operating speeds under which the engine or motor is able to output the most power, that is, the maximum energy per unit of time. This usually means that maximum a ...
. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines.
History
The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed toScottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later two-stroke engines, his had a separate charging cylinder. The crankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.
Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/a ...
-scavenged engine, employing the area below the piston as a charging pump, is generally credited to Englishman Joseph Day. On 31 December 1879, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
Karl Benz
Carl Friedrich Benz (; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929), sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and fir ...
produced a two-stroke gas engine, for which he received a patent in 1880 in Germany. The first truly practical two-stroke engine is attributed to Yorkshireman Alfred Angas Scott
Alfred Angas Scott (1875–1923) was a British motorcycle designer, inventor and founder of the Scott Motorcycle Company. A prolific inventor, he took out over 50 patents between 1897 and 1920, mostly concerning two-stroke engines and road vehic ...
, who started producing twin-cylinder water-cooled
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant
Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and non ...
motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s in 1908.
Two-stroke gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
engines with electrical spark ignition are particularly useful in lightweight or portable applications such as chainsaws
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruning, ...
and motorcycles. However, when weight and size are not an issue, the cycle's potential for high thermodynamic efficiency makes it ideal for diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
compression ignition engines operating in large, weight-insensitive applications, such as marine propulsion, railway locomotives, and electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transmi ...
. In a two-stroke engine, the exhaust gases transfer less heat to the cooling system than a four-stroke, which means more energy to drive the piston, and if present, a turbocharger.
Emissions
Crankcase-compression two-stroke engines, such as common small gasoline-powered engines, are lubricated by a petroil mixture in a total-loss system. Oil is mixed in with their petrol fuel beforehand, in a fuel-to-oil ratio of around 32:1. This oil then forms emissions, either by being burned in the engine or as droplets in the exhaust, historically resulting in more exhaust emissions, particularly hydrocarbons, than four-stroke engines of comparable power output. The combined opening time of the intake and exhaust ports in some two-stroke designs can also allow some amount of unburned fuel vapors to exit in the exhaust stream. The high combustion temperatures of small, air-cooled engines may also produce NOx emissions. However, with direct fuel injection and a sump-based lubrication system, a modern two-stroke engine can produce air pollution no worse than a four-stroke, and can achieve higher thermodynamic efficiency.Applications

power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
are design priorities. By mixing oil with fuel, they can operate in any orientation as the oil reservoir does not depend on gravity.
A number of mainstream automobile manufacturers have used two-stroke engines in the past, including the Swedish Saab and German manufacturers DKW
DKW (''Dampf-Kraft-Wagen'', en, "steam-powered car", also ''Deutsche Kinder-Wagen'' en, "German children's car". ''Das-Kleine-Wunder'', en, "the little wonder" or ''Des-Knaben-Wunsch'', en, "the boy's wish"- from when the company built to ...
, Auto-Union, VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau
HQM Sachsenring GmbH is a Zwickau-based company that supplies chassis and body parts to the automotive industry. The company was named after the Sachsenring race track. Founded as VEB Sachsenring after the end of World War II, Sachsenring was one ...
, VEB Automobilwerk Eisenach
The Automobilwerk Eisenach (AWE) was an automobile manufacturer in Eisenach, Germany.
History
Fahrzeugfabrik Eisenach
Heinrich Ehrhardt founded the Fahrzeugfabrik Eisenach (FFE) in Eisenach on 3 December 1896 as a stock company. Init ...
, and VEB Fahrzeug- und Jagdwaffenwerk „Ernst Thälmann. The Japanese manufacturers Suzuki
is a Japan, Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, All-terrain vehicle, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard motor, outboard marine engines, wheelchairs ...
and Subaru
( or ; ) is the automaker, automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate (company), conglomerate Subaru Corporation (formerly known as Fuji Heavy Industries), the Automotive industry#By manufacturer, twenty-first ...
did the same in the 1970s. Production of two-stroke cars ended in the 1980s in the West, due to increasingly stringent regulation of air pollution. Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
countries continued until around 1991, with the Trabant and Wartburg
The Wartburg () is a castle originally built in the Middle Ages. It is situated on a precipice of to the southwest of and overlooking the town of Eisenach, in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It was the home of St. Elisabeth of Hungary, the p ...
in East Germany.
Two-stroke engines are still found in a variety of small propulsion applications, such as outboard motors, small on- and off-road
Off-roading is the activity of driving or riding in a vehicle on unpaved surfaces such as sand, gravel, riverbeds, mud, snow, rocks, and other natural terrain. Types of off-roading range in intensity, from leisure drives with unmodified vehicl ...
motorcycles, moped
A moped ( ) is a type of small motorcycle, generally having a less stringent licensing requirement than full motorcycles or automobiles. The term used to mean a similar vehicle except with both bicycle pedals and a motorcycle engine. Mopeds typic ...
s, scooters, tuk-tuks, snowmobiles, go-karts
A go-kart, also written as go-cart (often referred to as simply a kart), is a type of sports car, close wheeled car, open-wheel car or quadracycle. Go-karts come in all shapes and forms, from non-motorised models to high-performance racing ...
, ultralight and model airplanes. Particularly in developed countries, pollution regulations have meant that their use for many of these applications is being phased out. Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a product ...
, for instance, ceased selling two-stroke off-road motorcycles in the United States in 2007, after abandoning road-going models considerably earlier.
Due to their high power-to-weight ratio and ability to be used in any orientation, two-stroke engines are common in handheld outdoor power tools including leaf blowers
A leaf blower, commonly known as a blower, is a device that propels air out of a nozzle to move debris such as leaves and grass cuttings. Leaf blowers are powered by electric or gasoline motors. Gasoline models have traditionally been two-st ...
, chainsaws
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruning, ...
, and string trimmers.
Two-stroke diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-call ...
s are found mostly in large industrial and marine applications, as well as some trucks and heavy machinery.
Different two-stroke design types
 Although the principles remain the same, the mechanical details of various two-stroke engines differ depending on the type. The design types vary according to the method of introducing the charge to the cylinder, the method of scavenging the
Although the principles remain the same, the mechanical details of various two-stroke engines differ depending on the type. The design types vary according to the method of introducing the charge to the cylinder, the method of scavenging the cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
(exchanging burnt exhaust for fresh mixture) and the method of exhausting the cylinder.
Piston-controlled inlet port
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
port is the simplest of the designs and the most common in small two-stroke engines. All functions are controlled solely by the piston covering and uncovering the ports as it moves up and down in the cylinder. In the 1970s, Yamaha Yamaha may refer to:
* Yamaha Corporation, a Japanese company with a wide range of products and services, established in 1887. The company is the largest shareholder of Yamaha Motor Company (below).
** Yamaha Music Foundation, an organization estab ...
worked out some basic principles for this system. They found that, in general, widening an exhaust port increases the power by the same amount as raising the port, but the power band does not narrow as it does when the port is raised. However, a mechanical limit exists to the width of a single exhaust port, at about 62% of the bore diameter for reasonable piston ring life. Beyond this, the piston rings bulge into the exhaust port and wear quickly. A maximum 70% of bore width is possible in racing engines, where rings are changed every few races. Intake duration is between 120 and 160°. Transfer port time is set at a minimum of 26°. The strong, low-pressure pulse of a racing two-stroke expansion chamber can drop the pressure to -7 psi when the piston is at bottom dead center, and the transfer ports nearly wide open. One of the reasons for high fuel consumption in two-strokes is that some of the incoming pressurized fuel-air mixture is forced across the top of the piston, where it has a cooling action, and straight out the exhaust pipe. An expansion chamber with a strong reverse pulse stops this outgoing flow.
A fundamental difference from typical four-stroke engines is that the two-stroke's crankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.
Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/a ...
is sealed and forms part of the induction process in gasoline and hot bulb engines. Diesel two-strokes often add a Roots blower
The Roots-type blower is a
positive displacement lobe pump which operates by pumping a fluid with a pair of meshing lobes resembling a set of stretched gears. Fluid is trapped in pockets surrounding the lobes and carried from the intake si ...
or piston pump for scavenging.
Reed inlet valve
check valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have t ...
commonly fitted in the intake tract of the piston-controlled port. It allows asymmetric intake of the fuel charge, improving power and economy, while widening the power band. Such valves are widely used in motorcycle, ATV, and marine outboard engines.
Rotary inlet valve
The intake pathway is opened and closed by a rotating member. A familiar type sometimes seen on small motorcycles is a slotted disk attached to thecrankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
, which covers and uncovers an opening in the end of the crankcase, allowing charge to enter during one portion of the cycle (called a disc valve).
Another form of rotary inlet valve used on two-stroke engines employs two cylindrical members with suitable cutouts arranged to rotate one within the other - the inlet pipe having passage to the crankcase only when the two cutouts coincide. The crankshaft itself may form one of the members, as in most glow-plug model engines. In another version, the crank disc is arranged to be a close-clearance fit in the crankcase, and is provided with a cutout that lines up with an inlet passage in the crankcase wall at the appropriate time, as in Vespa
Vespa () is an Italian luxury brand of scooter (motorcycle), scooters and mopeds manufactured by Piaggio. The name means wasp in Italian. The Vespa has evolved from a single model motor scooter manufactured in 1946 by Piaggio & Co. S.p.A. of ...
motor scooters.
The advantage of a rotary valve is that it enables the two-stroke engine's intake timing to be asymmetrical, which is not possible with piston-port type engines. The piston-port type engine's intake timing opens and closes before and after top dead center at the same crank angle, making it symmetrical, whereas the rotary valve allows the opening to begin and close earlier.
Rotary valve engines can be tailored to deliver power over a wider speed range or higher power over a narrower speed range than either a piston-port or reed-valve engine. Where a portion of the rotary valve is a portion of the crankcase itself, of particular importance, no wear should be allowed to take place.
Cross-flow scavenging
 In a cross-flow engine, the transfer and exhaust ports are on opposite sides of the cylinder, and a deflector on the top of the piston directs the fresh intake charge into the upper part of the cylinder, pushing the residual exhaust gas down the other side of the deflector and out the exhaust port.
The deflector increases the piston's weight and exposed surface area, and the fact that it makes piston cooling and achieving an effective combustion chamber shape more difficult is why this design has been largely superseded by uniflow scavenging after the 1960s, especially for motorcycles, but for smaller or slower engines using direct injection, the deflector piston can still be an acceptable approach.
In a cross-flow engine, the transfer and exhaust ports are on opposite sides of the cylinder, and a deflector on the top of the piston directs the fresh intake charge into the upper part of the cylinder, pushing the residual exhaust gas down the other side of the deflector and out the exhaust port.
The deflector increases the piston's weight and exposed surface area, and the fact that it makes piston cooling and achieving an effective combustion chamber shape more difficult is why this design has been largely superseded by uniflow scavenging after the 1960s, especially for motorcycles, but for smaller or slower engines using direct injection, the deflector piston can still be an acceptable approach.
Loop scavenging
cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern ov ...
, then follows the curvature of the combustion chamber, and then is deflected downward.
This not only prevents the fuel/air mixture from traveling directly out the exhaust port, but also creates a swirling turbulence which improves combustion efficiency, power, and economy.
Usually, a piston deflector is not required, so this approach has a distinct advantage over the cross-flow scheme (above).
Often referred to as "Schnuerle" (or "Schnürle") loop scavenging after Adolf Schnürle, the German inventor of an early form in the mid-1920s, it became widely adopted in that country during the 1930s and spread further afield after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Loop scavenging is the most common type of fuel/air mixture transfer used on modern two-stroke engines. Suzuki was one of the first manufacturers outside of Europe to adopt loop-scavenged, two-stroke engines. This operational feature was used in conjunction with the expansion chamber exhaust developed by German motorcycle manufacturer, MZ, and Walter Kaaden.
Loop scavenging, disc valves, and expansion chambers worked in a highly coordinated way to significantly increase the power output of two-stroke engines, particularly from the Japanese manufacturers Suzuki, Yamaha, and Kawasaki. Suzuki and Yamaha enjoyed success in Grand Prix motorcycle racing in the 1960s due in no small way to the increased power afforded by loop scavenging.
An additional benefit of loop scavenging was the piston could be made nearly flat or slightly domed, which allowed the piston to be appreciably lighter and stronger, and consequently to tolerate higher engine speeds. The "flat top" piston also has better thermal properties and is less prone to uneven heating, expansion, piston seizures, dimensional changes, and compression losses.
SAAB built 750- and 850-cc three-cylinder engines based on a DKW design that proved reasonably successful employing loop charging. The original SAAB 92 had a two-cylinder engine of comparatively low efficiency. At cruising speed, reflected-wave, exhaust-port blocking occurred at too low a frequency. Using the asymmetrical three-port exhaust manifold employed in the identical DKW engine improved fuel economy.
The 750-cc standard engine produced 36 to 42 hp, depending on the model year. The Monte Carlo Rally variant, 750-cc (with a filled crankshaft for higher base compression), generated 65 hp. An 850-cc version was available in the 1966 SAAB Sport (a standard trim model in comparison to the deluxe trim of the Monte Carlo).
Base compression comprises a portion of the overall compression ratio of a two-stroke engine.
Work published at SAE in 2012 points that loop scavenging is under every circumstance more efficient than cross-flow scavenging.
Uniflow scavenging
Detroit Diesel
Detroit Diesel Corporation (DDC) is an American diesel engine manufacturer headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is a subsidiary of Daimler Truck North America, which is itself a wholly owned subsidiary of the mulitinational Da ...
), certain small marine two-stroke engines (Gray Marine
Gray Marine Motor Company was a U.S. manufacturer of marine engines between 1910 and 1967. These ranged from one to six cylinders in both gas and later diesel layouts, which were used in pleasure boats, work boats, and military craft.
Gray w ...
), certain railroad two-stroke diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving whee ...
s ( Electro-Motive Diesel) and large marine two-stroke main propulsion engines (Wärtsilä
Wärtsilä Oyj Abp (), trading internationally as Wärtsilä Corporation, is a Finnish company which manufactures and services power sources and other equipment in the marine and energy markets. The core products of Wärtsilä include technol ...
). Ported types are represented by the opposed piston
An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and ...
design in which two pistons are in each cylinder, working in opposite directions such as the Junkers Jumo 205 and Napier Deltic. The once-popular split-single
In internal combustion engines, a split-single design is a type of two-stroke where two cylinders share a single combustion chamber.
The first production split-single engine was built in 1918 and the design was used on several motorcycles and ca ...
design falls into this class, being effectively a folded uniflow. With advanced-angle exhaust timing, uniflow engines can be supercharged with a crankshaft-driven (piston or Roots) blower.
Stepped piston engine
The piston of this engine is "top-hat"-shaped; the upper section forms the regular cylinder, and the lower section performs a scavenging function. The units run in pairs, with the lower half of one piston charging an adjacent combustion chamber. The upper section of the piston still relies on total-loss lubrication, but the other engine parts are sump lubricated with cleanliness and reliability benefits. The mass of the piston is only about 20% more than a loop-scavenged engine's piston because skirt thicknesses can be less.Power-valve systems
Many modern two-stroke engines employ a power-valve system. The valves are normally in or around the exhaust ports. They work in one of two ways; either they alter the exhaust port by closing off the top part of the port, which alters port timing, such as Rotax R.A.V.E,Yamaha Yamaha may refer to:
* Yamaha Corporation, a Japanese company with a wide range of products and services, established in 1887. The company is the largest shareholder of Yamaha Motor Company (below).
** Yamaha Music Foundation, an organization estab ...
YPVS, Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a product ...
RC-Valve, Kawasaki K.I.P.S., Cagiva
Cagiva is an Italian motorcycle manufacturer. It was founded in 1950 by Giovanni Castiglioni in Varese, originally producing small metal components. Giovanni's sons, Claudio and Gianfranco Castiglioni, went into the motorcycle industry in 1978. ...
C.T.S., or Suzuki
is a Japan, Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, All-terrain vehicle, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard motor, outboard marine engines, wheelchairs ...
AETC systems, or by altering the volume of the exhaust, which changes the resonant frequency of the expansion chamber
On a two-stroke engine, an expansion chamber or tuned pipe is a tuned exhaust system used to enhance its power output by improving its volumetric efficiency.
History
Expansion chambers were invented and successfully manufactured by Limbach, a ...
, such as the Suzuki
is a Japan, Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, All-terrain vehicle, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard motor, outboard marine engines, wheelchairs ...
SAEC and Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a product ...
V-TACS system. The result is an engine with better low-speed power without sacrificing high-speed power. However, as power valves are in the hot gas flow, they need regular maintenance to perform well.
Direct injection
Direct injection has considerable advantages in two-stroke engines. In carburetted two-strokes, a major problem is a portion of the fuel/air mixture going directly out, unburned, through the exhaust port, and direct injection effectively eliminates this problem. Two systems are in use, low-pressure air-assisted injection and high-pressure injection. Since the fuel does not pass through the crankcase, a separate source of lubrication is needed.Diesel
 Diesel engines rely solely on the heat of compression for ignition. In the case of Schnuerle-ported and loop-scavenged engines, intake and exhaust happen via piston-controlled ports. A uniflow diesel engine takes in air via scavenge ports, and exhaust gases exit through an overhead poppet valve. Two-stroke diesels are all scavenged by forced induction. Some designs use a mechanically driven Roots blower, whilst marine diesel engines normally use exhaust-driven turbochargers, with electrically driven auxiliary blowers for low-speed operation when exhaust turbochargers are unable to deliver enough air.
Marine two-stroke diesel engines directly coupled to the propeller are able to start and run in either direction as required. The fuel injection and valve timing are mechanically readjusted by using a different set of cams on the camshaft. Thus, the engine can be run in reverse to move the vessel backwards.
Diesel engines rely solely on the heat of compression for ignition. In the case of Schnuerle-ported and loop-scavenged engines, intake and exhaust happen via piston-controlled ports. A uniflow diesel engine takes in air via scavenge ports, and exhaust gases exit through an overhead poppet valve. Two-stroke diesels are all scavenged by forced induction. Some designs use a mechanically driven Roots blower, whilst marine diesel engines normally use exhaust-driven turbochargers, with electrically driven auxiliary blowers for low-speed operation when exhaust turbochargers are unable to deliver enough air.
Marine two-stroke diesel engines directly coupled to the propeller are able to start and run in either direction as required. The fuel injection and valve timing are mechanically readjusted by using a different set of cams on the camshaft. Thus, the engine can be run in reverse to move the vessel backwards.
Lubrication
Many two-stroke engines use theircrankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.
Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/a ...
to pressurize the air-fuel mixture before transfer to the cylinder. Unlike four-stroke engines, they cannot be lubricated by oil contained in the crankcase and sump: lubricating oil
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, t ...
would be swept up and burnt with the fuel. Fuels supplied to two-stroke engines are mixed with oil so that it can coat the cylinders and bearing surfaces along its path. The ratio of gasoline to oil ranges from 25:1 to 50:1 by volume.
Oil remaining in the mixture is burnt with the fuel and results in a familiar blue smoke and odor. Two-stroke oils, which became available in the 1970s, are specifically designed to mix with petrol and be burnt with minimal unburnt oil or ash. This led to a marked reduction in spark plug fouling, which had previously been a problem in two-stroke engines.
Other two-stroke engines might pump lubrication from a separate tank of two-stroke oil. The supply of this oil is controlled by the throttle position and engine speed. Examples are found in Yamaha's PW80 (Pee-wee), and many two-stroke snowmobiles. The technology is referred to as auto-lube. This is still a total-loss system with the oil being burnt the same as in the premix system. Given that the oil is not properly mixed with the fuel when burned in the combustion chamber, it provides slightly more efficient lubrication. This lubrication method eliminates the user's need to mix the gasoline at every refill, makes the motor much less susceptible to atmospheric conditions (ambient temperature, elevation), and ensures proper engine lubrication, with less oil at light loads (such as idle) and more oil at high loads (full throttle). Some companies, such as Bombardier, had some oil-pump designs have no oil injected at idle to reduce smoke levels, as the loading on the engine parts was light enough to not require additional lubrication beyond the low levels that the fuel provides. Ultimately, oil injection is still the same as premixed gasoline in that the oil is burnt in the combustion chamber (albeit not as completely as premix) and the gas is still mixed with the oil, although not as thoroughly as in premix. This method requires extra mechanical parts to pump the oil from the separate tank, to the carburetor or throttle body. In applications where performance, simplicity, and/or dry weight are significant considerations, the premix lubrication method is almost always used. For example, a two-stroke engine in a motocross bike pays major consideration to performance, simplicity, and weight. Chainsaws and brush cutters must be as lightweight as possible to reduce user fatigue and hazard.
Crankcase compression two-stroke engines suffer oil starvation if rotated at speed with the throttle closed. Motorcycles descending long hills and perhaps when decelerating gradually from high speed by changing down through the gears are examples. Two-stroke cars (such as those that were popular in Eastern Europe in the mid-20th century) were usually fitted with freewheel
Freewheel mechanism
In mechanical or automotive engineering, a freewheel or overrunning clutch is a device in a transmission that disengages the driveshaft from the driven shaft when the driven shaft rotates faster than the driveshaft. An ov ...
mechanisms in the powertrain, allowing the engine to idle when the throttle was closed and requiring using brakes to slow down.
Large two-stroke engines, including diesels, normally use a sump lubrication system similar to four-stroke engines. The cylinder must be pressurized, but this is not done from the crankcase, but by an ancillary Roots-type blower or a specialized turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
(usually a turbo-compressor system) which has a "locked" compressor for starting (and during which it is powered by the engine's crankshaft), but which is "unlocked" for running (and during which it is powered by the engine's exhaust gases flowing through the turbine).
Two-stroke reversibility
For the purpose of this discussion, it is convenient to think in motorcycle terms, where the exhaust pipe faces into the cooling air stream, and the crankshaft commonly spins in the same axis and direction as do the wheels i.e. "forward". Some of the considerations discussed here apply to four-stroke engines (which cannot reverse their direction of rotation without considerable modification), almost all of which spin forward, too. It is also useful to note that the "front" and "back" faces of the piston are - respectively - the exhaust port and intake port sides of it, and are not to do with the top or bottom of the piston. Regular gasoline two-stroke engines can run backward for short periods and under light load with little problem, and this has been used to provide a reversing facility in microcars, such as theMesserschmitt KR200
The Messerschmitt KR200, or ''Kabinenroller'' (Cabin Scooter), is a three-wheeled bubble car designed by the aircraft engineer Fritz Fend and produced in the factory of the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt from 1955 until 1964.
History
...
, that lacked reverse gearing. Where the vehicle has electric starting, the motor is turned off and restarted backward by turning the key in the opposite direction. Two-stroke golf carts have used a similar system. Traditional flywheel magnetos (using contact-breaker points, but no external coil) worked equally well in reverse because the cam controlling the points is symmetrical, breaking contact before top dead center equally well whether running forward or backward. Reed-valve engines run backward just as well as piston-controlled porting, though rotary valve engines have asymmetrical inlet timing and do not run very well.
Serious disadvantages exist for running many engines backward under load for any length of time, and some of these reasons are general, applying equally to both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. This disadvantage is accepted in most cases where cost, weight, and size are major considerations. The problem comes about because in "forward" running, the major thrust face of the piston is on the back face of the cylinder, which in a two-stroke particularly, is the coolest and best-lubricated part. The forward face of the piston in a trunk engine
Trunk may refer to:
Biology
* Trunk (anatomy), synonym for torso
* Trunk (botany), a tree's central superstructure
* Trunk of corpus callosum, in neuroanatomy
* Elephant trunk, the proboscis of an elephant
Computing
* Trunk (software), in re ...
is less well-suited to be the major thrust face, since it covers and uncovers the exhaust port in the cylinder, the hottest part of the engine, where piston lubrication is at its most marginal. The front face of the piston is also more vulnerable since the exhaust port, the largest in the engine, is in the front wall of the cylinder. Piston skirts and rings risk being extruded into this port, so having them pressing hardest on the opposite wall (where there are only the transfer ports in a crossflow engine) is always best and support is good. In some engines, the small end
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a reciprocating engine, piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank (mechanism), crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the ...
is offset to reduce thrust in the intended rotational direction and the forward face of the piston has been made thinner and lighter to compensate, but when running backward, this weaker forward face suffers increased mechanical stress it was not designed to resist.Ross and Ungar, "On Piston Slap as a Source of Engine Noise," ASME Paper This can be avoided by the use of crosshead
In mechanical engineering, a crosshead is a mechanical joint used as part of the slider-crank linkages of long reciprocating engines (either internal combustion or steam) and reciprocating compressors to eliminate sideways force on the piston. ...
s and also using thrust bearings to isolate the engine from end loads.
Large two-stroke ship diesels are sometimes made to be reversible. Like four-stroke ship engines (some of which are also reversible), they use mechanically operated valves, so require additional camshaft mechanisms. These engines use crossheads to eliminate sidethrust on the piston and isolate the under-piston space from the crankcase.
On top of other considerations, the oil pump of a modern two-stroke may not work in reverse, in which case the engine suffers oil starvation within a short time. Running a motorcycle engine backward is relatively easy to initiate, and in rare cases, can be triggered by a back-fire. It is not advisable.
Model airplane engines with reed valves can be mounted in either tractor or pusher configuration without needing to change the propeller. These motors are compression ignition, so no ignition timing issues and little difference between running forward and running backward are seen.
See also
*Bourke engine
The Bourke engine was an attempt by Russell Bourke, in the 1920s, to improve the two-stroke internal combustion engine. Despite finishing his design and building several working engines, the onset of World War II, lack of test results, and the ...
* Four-stroking
Four-stroking is a condition of two-stroke engines where combustion occurs every ''four'' strokes or more, rather than every two. Though normal in some instances at idle, extremely high engine speeds, and when letting off the throttle, such firi ...
* Junkers Jumo 205
* Kadenacy effect
* Rolls-Royce Crecy
The Rolls-Royce Crecy was a British experimental two-stroke, 90-degree, V12, liquid-cooled aero-engine of 1,593.4 cu.in (26.11 L) capacity, featuring sleeve valves and direct petrol injection. Initially intended for a high-speed "sprint" i ...
* Rotary engine
* Twingle engine
In internal combustion engines, a split-single design is a type of two-stroke where two cylinders share a single combustion chamber.
The first production split-single engine was built in 1918 and the design was used on several motorcycles and ca ...
* Stroke (engine)
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings:
* A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa.
* Th ...
** Two- and four-stroke engines Two-and-four-stroke engines are engines that combine elements from both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. They usually incorporate two pistons.
M4+2 engine
The M4+2 engine, also known as the double-piston internal combustion engine, is a new ty ...
** Four-stroke engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directio ...
** Five-stroke engine
Five-stroke engine is currently a concept engine invented by Gerhard Schmitz in 2000. Schmitz's concept is being developed by Ilmor Engineering. Ilmor's prototype is an internal combustion engine that uses a solid cylinder block with electric m ...
(uncommon)
** Six-stroke engine The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced m ...
* Wärtsilä-Sulzer RTA96-C
The Wärtsilä RT-flex96C is a two-stroke turbocharged low-speed diesel engine designed by the Finnish manufacturer Wärtsilä. It is designed for large container ships that run on heavy fuel oil. Its largest 14-cylinder version is 13.5 meters ...
* Wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and desi ...
References
Further reading
* Frank Jardine (Alcoa): "Thermal Expansion in Automotive-Engine Design", SAE paper 300010 * G P Blair et al. (Univ of Belfast), R Fleck (Mercury Marine), "Predicting the Performance Characteristics of Two-Cycle Engines Fitted with Reed Induction Valves", SAE paper 790842 * G Bickle et al. (ICT Co), R Domesle et al. (Degussa AG): "Controlling Two-Stroke Engine Emissions", Automotive Engineering International (SAE) Feb 2000:27-32. * BOSCH, "Automotive Manual", 2005, Section: Fluid's Mechanics, Table 'Discharge from High-Pressure Deposits'.External links
*Two-Stroke Engine
at How Stuff Works * . {{DEFAULTSORT:Two-Stroke All articles with unsourced statements Engine technology Internal combustion piston engines Motorcycle engines Piston ported engines